Global Economic Trends and Their Impact on Agriculture by 2030
To determine the anticipated trends of agricultural software development in the food and agriculture markets by 2030, we looked at the OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030.
Researchers anticipate a decline in demand, but maintaining steady pricing will depend on increasing the efficiency of crop and livestock production.
The agricultural sector must utilise innovative technical solutions to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and address consumer income levels, changing food preferences and environmental concerns.
We can observe the annual GDP growth rate from 2021 to 2030 to understand the economic performance and trends of this decade in this chart:
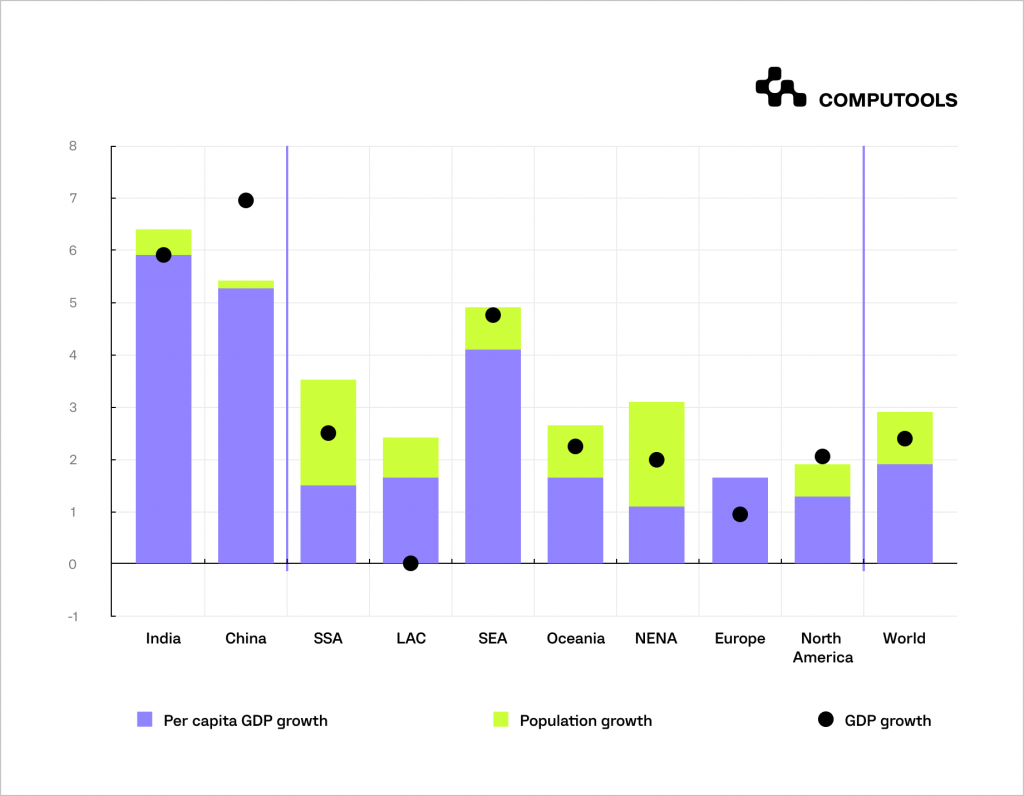
If we analyse this data, we see that the world’s economic conditions are dynamic and heterogeneous. Different regions show different growth rates.
This is due to different factors, including the level of technological development, the attractiveness of investment in the region, and its political stability.
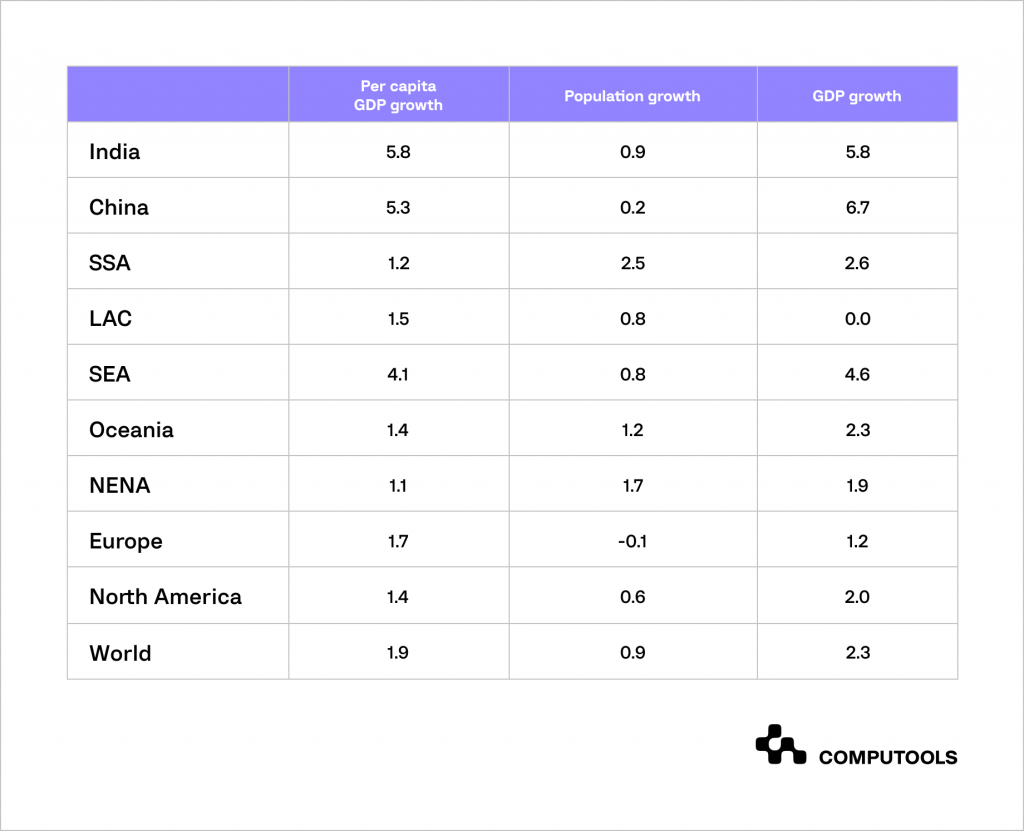
India and China show high growth rates of GDP per capita and total GDP, indicating their dynamic economic development.
The SSA, LAC, SEA and NENA regions also show positive growth rates, albeit more moderate than in Asia.
Europe and North America show lower growth rates, indicating their mature stage of economic development.
In most regions, there is a positive correlation between population growth and GDP growth. An increase in population stimulates economic growth.
However, in Europe, population growth is negative, but GDP is still growing. What does this tell us?
Economic growth can be driven by factors other than population growth, such as technological progress and increased labour productivity.
It is innovation and the introduction of AI usage for business that allow countries to increase productivity, create new jobs and improve the quality of life of the population.
One of the most promising areas of technological development is the role of Artificial Intelligence.
How to Use AI in the Agriculture Industry
The advent of quickly developing technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), gives agricultural players another useful instrument to tackle these obstacles head-on and achieve increased productivity and effectiveness across their enterprises.
Particularly generative AI, or gen AI, has drawn the interest of numerous influential figures in agriculture and other fields and has the potential to bring about profound change.
According to McKinsey, agricultural business in the $4 trillion global food production sector can use gen AI to enhance its AI initiatives fully.
Improving labour and input costs and yields on the acre and increasing productivity and operational efficiencies can produce economic value for the enterprise.
Alternatively, it can create value for the individual by increasing sales growth and yields on the enterprise.
According to their estimate, AI has the potential to generate $150 billion in the latter sector and $100 billion in the former.
See how to tackle AI in agriculture industry:
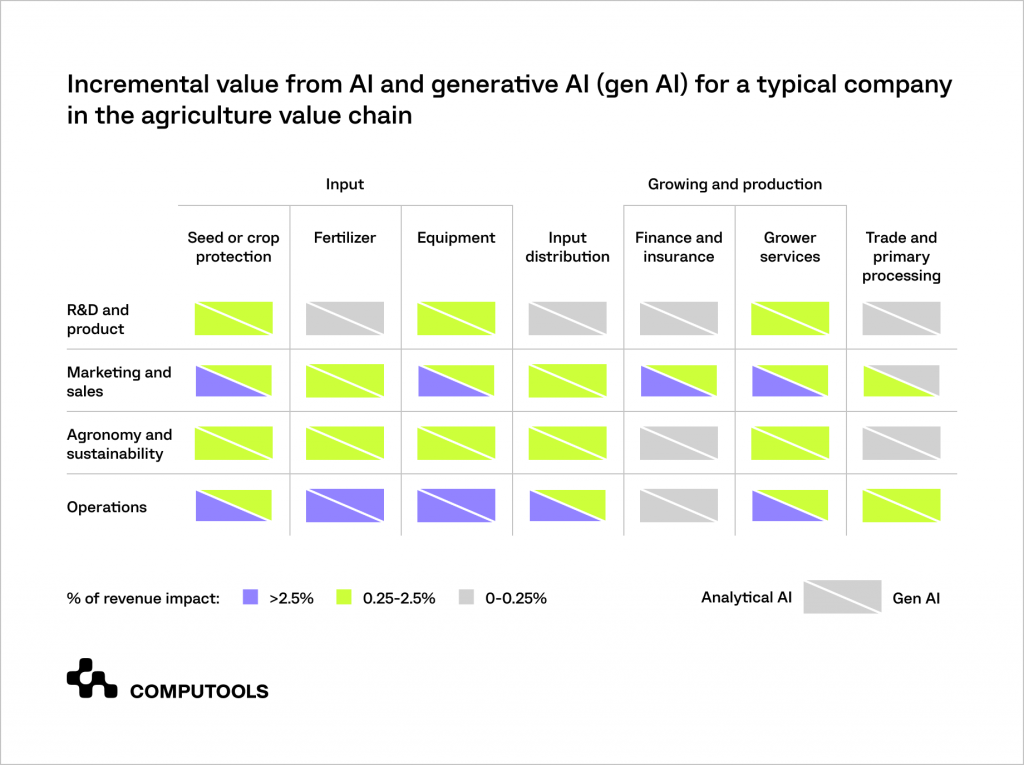
Applications that can handle vast and varied volumes of unstructured data, such as meteorological and geographic data, and carry out several tasks are referred to as “generative AI” (gen AI).
By finding patterns in massive data sets, generative AI can produce fresh discoveries, particularly in challenging jobs like agronomy, marketing, code development, and molecular research.
Analytical AI, on the other hand, is concerned with solving particular issues and forecasts outcomes using well-defined rules and organised data.
Customer segmentation, sentiment analysis, and sales forecasting are a few applications of analytical AI.
Generative AI:
• Processes large amounts of unstructured data, including geospatial and weather data.
• Performs multiple tasks.
• Able to create new insights by identifying patterns in data.
• Applies to complex tasks such as molecular research, marketing, agronomy, and code writing.
Analytical AI:
• Solves specific problems.
• Makes predictions based on structured data and well-defined rules.
• Examples of uses: sales forecasting, customer segmentation, and sentiment analysis.
Because of the large amount of unstructured data accumulated in agriculture, this industry is ideally suited for applying AI and generative AI.
Challenges for Agriculture Industry
Of the numerous problems facing agricultural business, three are particularly prominent because of their worldwide reach and economic influence:
Of the numerous problems facing agricultural business, three are particularly prominent because of their worldwide reach and economic influence:
1. Pests
Costing at least $70 billion a year, pests consume over 40% of agricultural yield worldwide.
Fruit flies damage orchards, or locust swarms destroy African fields — the effects are widespread and have enormous financial consequences.
2. Soil Quality and Irrigation
Approximately 33% of Earth’s soil is degraded, which reduces its capacity to support crop growth and results in a $400 billion loss.
A shortage of water and ineffective irrigation further reduce agricultural productivity. Sixty percent of the freshwater available worldwide is lost to faulty irrigation systems, despite being used for agriculture.
3. Weeds
In spite of improvements in farming techniques, weeds significantly reduce crop yield and quality.
Approximately 1800 types of weeds cause a 31.5% reduction in plant productivity, resulting in yearly losses of roughly $32 billion.
Moreover, AI software solutions can reduce the need for significant numbers of workers, complex logistical processes, and lengthy research and development. Agricultural businesses are also interested in personalized and low-cost services.
For example, generative AI can create trial scenarios by analysing vast amounts of data on weather, soil conditions, and threats from pests and diseases, and analytical AI models can simulate these scenarios.
Research indicates that while many firms have traditionally concentrated their agricultural software development efforts on support activities, the greatest advantages of AI in agriculture come from analytical AI and general AI in farming use cases in essential areas including R&D and product development, marketing and sales, agronomy and sustainability, and operations.
Although there are a lot of benefits of AI, there are also disadvantages associated with it. Data privacy concerns may arise as agriculture becomes a hotbed for data collection, from below ground to crop level and above ground.
These difficulties highlight the necessity of cautious thought and governance to weigh the potential benefits of AI against its drawbacks.
This is exclusive to AI applications in agriculture and all other industries that use AI.
Predictions on the Impact of AI Software
To support the importance of technology, here are five predictions about the future of AI in agriculture:
1. Data standardisation
Standardisation of data acquired from IoT devices and other sources is crucial, as the number of variables required for AI applications is growing due to the increased adoption of these devices.
Although most GIS software suppliers now allow their customers to include AI in their applications, models still require data as their input.
AI applications use structured and standardised data to train models, enhance accuracy and performance, and serve as the foundation for predictions and judgments.
A further expansion in the application of AI in agriculture will depend on continuous performance and accuracy development, which is why collecting standardised data will be a top priority.
2. Digitalisation of information
However, a sizable amount of agricultural data is still collected by hand (written, for instance) and is not yet computerised, organised, or standardised.
AI can help transform unstructured and non-digital data into digitally structured data that can be used further rather than just being kept.
The technology to make this happen already exists in AI models and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) software.
Agtech businesses are realising that it’s difficult to persuade farmers to enter data using their specific app; instead, it’s better to utilise technology that creates standardised data without requiring farmers to alter their routines.
3. Sustainable development
The main goals of sustainable agriculture are resource conservation, environmental preservation, and the optimal use of non-renewable resources.
Therefore, consider focusing on the highest yield per gallon of water, pound of nitrogen, or whichever input is the most limiting element, as opposed to having the highest output per acre.
Massive volumes of data must be gathered, processed, and transformed into useful insights in order to attain the highest level of sustainability and precision.
This is where artificial intelligence (AI) comes into play. Data-driven insights are provided by AI, which eliminates the need for guessing and “how I’ve always done it” aspects.
4. Innovation in agronomy
AI is changing how people farm worldwide, from spraying to weeding and many other in-crop uses.
By distinguishing between cultivated plants and weeds, technology allows for targeted pesticide application, minimising the need for pesticides.
Using mechanical actuation, Stout’s Smart Cultivator functions as an AI-powered in-row weeder that eliminates weeds without requiring huge field personnel or chemical use.
New AI-powered devices are unveiled every year. This is one area of the agriculture industry that is fast transforming.
5. Robots and automation
Many farms now use robots frequently. As AI and ML models get more sophisticated, more robots and on-farm automation can be implemented, which will help farmers reduce operational costs and address the labor problem in agriculture.
Many crops are already farmed with AI and ML-powered robots involved in specific stages of the process, from self-driving tractors to fully automated swarms of drones tending to fields. This will quickly spread throughout society.
Why a Reliable Software Engineering Partner with Subject Matter Expertise in Agriculture is Crucial
When developing software for the agricultural sector, choosing a reliable partner with subject matter expertise in this field is essential.
Specialised knowledge and experience give businesses that are just entering the market a big advantage.
1. Deep Industry Understanding
A partner with expertise in agriculture understands the unique needs and challenges faced by agri-businesses.
They know which data is critical, how to collect and process it correctly, and which technologies best suit specific tasks.
This helps avoid costly mistakes and trial-and-error phases arising when a company is new to the industry.
2. Effective Solutions for Specific Problems
Specialised partners offer solutions tailored to agriculture’s specific needs.
For example, we developed innovative AI software solutions for monitoring animal health in our case study with Alpha-Pig, a leading pig feed production firm.
By utilising AI development services, we created a system that improved farm management and increased productivity by 15%.
This type of AI software development addresses precise needs without the risks of untested solutions.
3. Advanced Technologies and Methods
Experienced developers in agriculture are familiar with cutting-edge technologies and methods that deliver the best results.
For instance, our AI software solutions for Alpha-Pig used AI algorithms, OpenCV for image processing, TensorFlow for machine learning, and various sensors to capture critical data.
These solutions are proven in real-world applications and offer more efficient and effective results.
4. Risk Reduction and Cost Efficiency
Partnering with a company experienced in agricultural software development services reduces the risks of implementing new technologies.
This avoids the costs of experimentation and errors that could occur with unproven solutions. A partner with industry expertise provides reliable and effective AI business solutions that streamline the process and enhance results.
5. Proven Case Studies
Successful case studies, such as our project Alpha-Pig, highlight the ability to handle real-world challenges.
Our AI software solutions improved health monitoring, boosted productivity, and enhanced profitability for Alpha-Pig. This demonstrates that a partner with subject matter expertise in agriculture can deliver significant value and improve business outcomes.
To explore how our AI-driven solutions can revolutionize your agricultural business, contact us today at info@computools.com.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”