Since 2023, the market for healthcare software has expanded significantly, and this growth is expected to last until at least 2028. Technological developments, digitisation, and national and international government efforts are the main drivers of this expansion. Extensive market data from organisations like Statista and Gartner amply illustrate the industry’s dynamic growth and opportunity for more investment.
The healthcare software industry, which is expected to develop at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 11%, was valued at more than USD 300 billion in 2023 and is expected to surpass USD 600 billion by 2028, according to Statista.
The need for specialised healthcare software solutions is being driven by the need for data management, telemedicine solutions, and regulatory compliance. Because of this, healthcare software has become one of the leading industries worldwide.
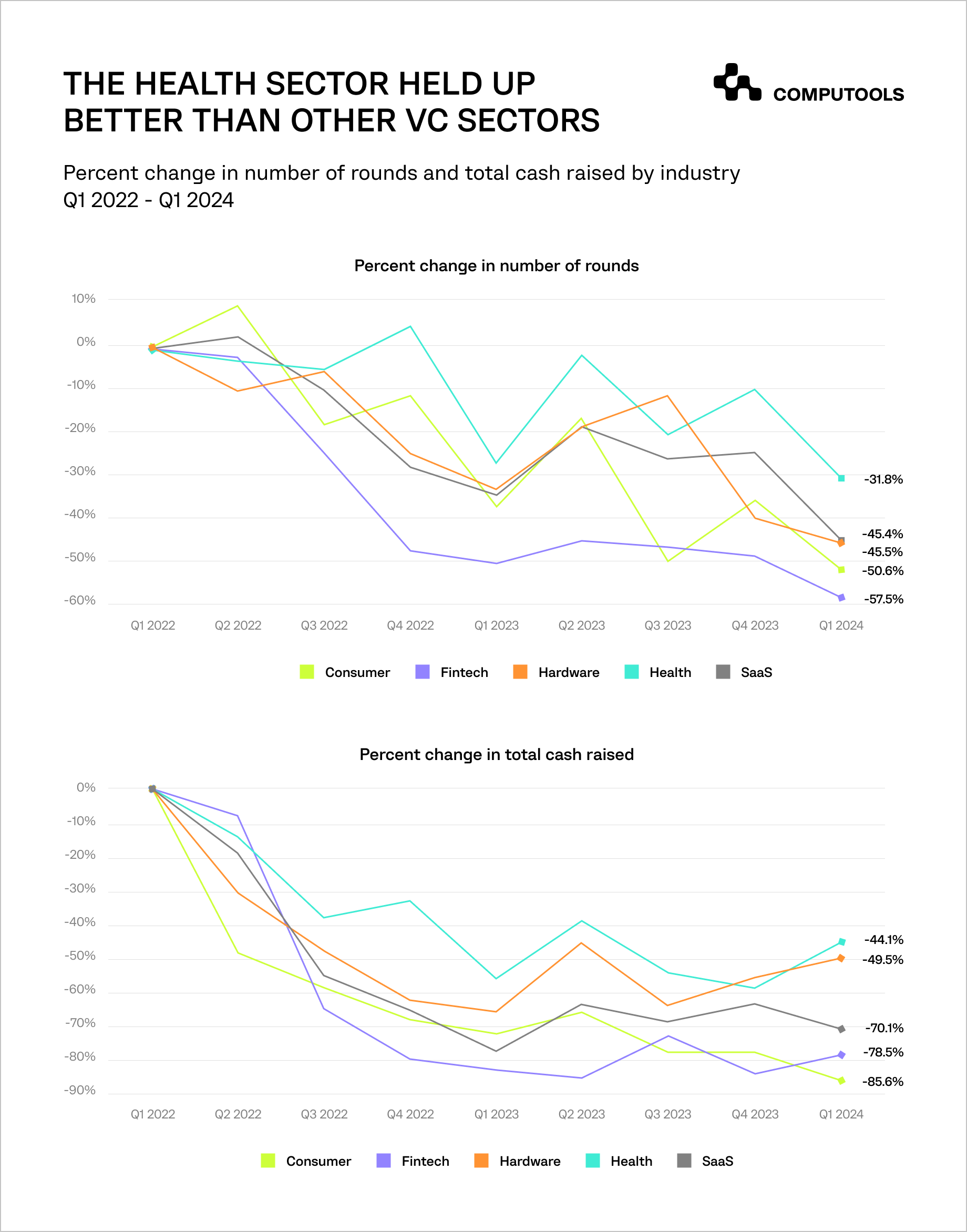
These graphs demonstrate the steadiness of the overall amount of money raised by the healthcare industry. Cash raised in the healthcare industry has declined by 44.1% since Q1 2022, which is less than the declines in fintech (78.5%) and SaaS (70.1%).
In the first quarter of 2024, capital spending in healthcare startups surged dramatically, growing 86% from the fourth quarter of 2023 to the first quarter of 2024, especially in the biotech/pharma area.
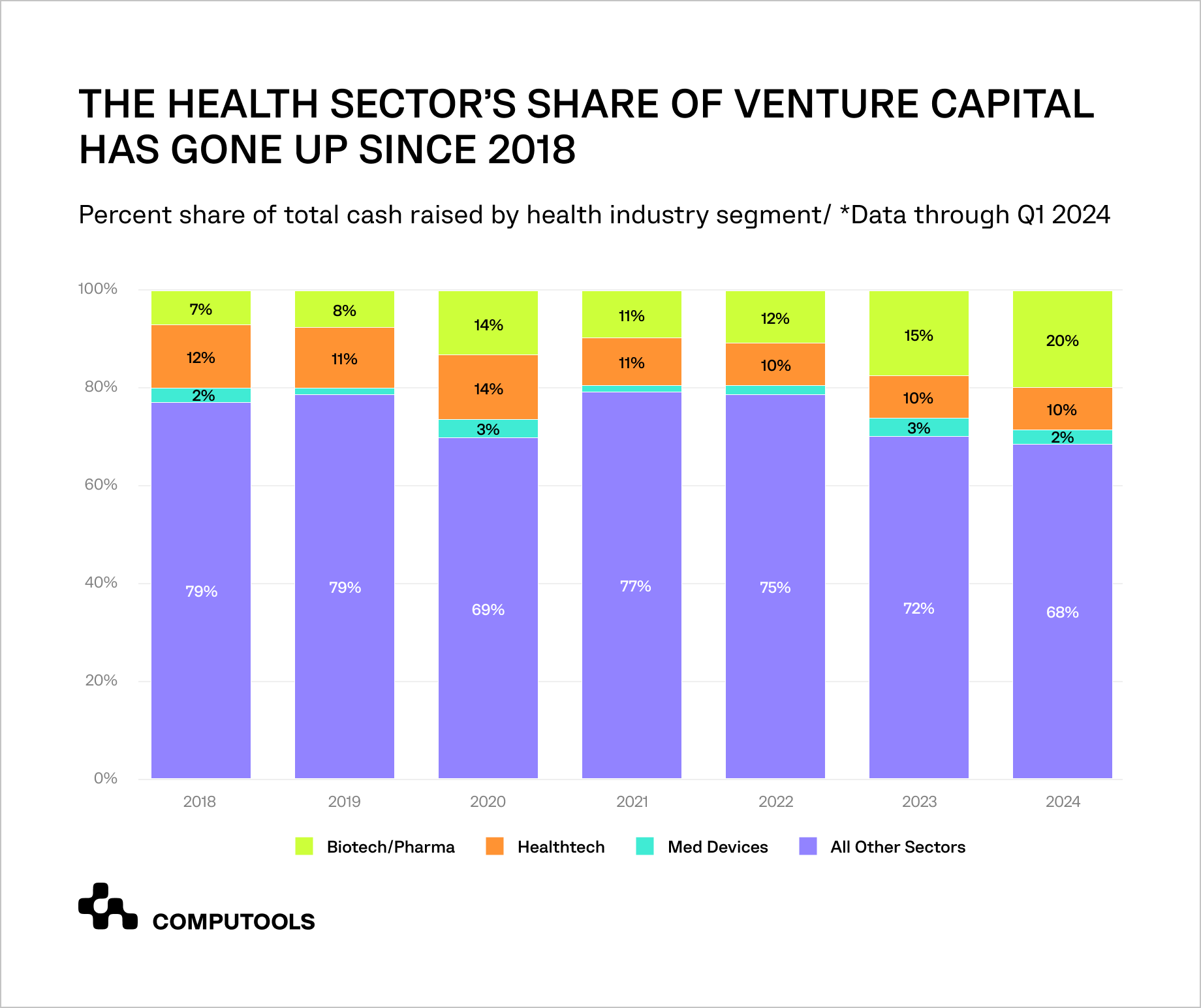
This is due to the fact that the percentage of venture capital allocated to startups in the health industry has increased from 21% in 2018 to 32% in 2024.
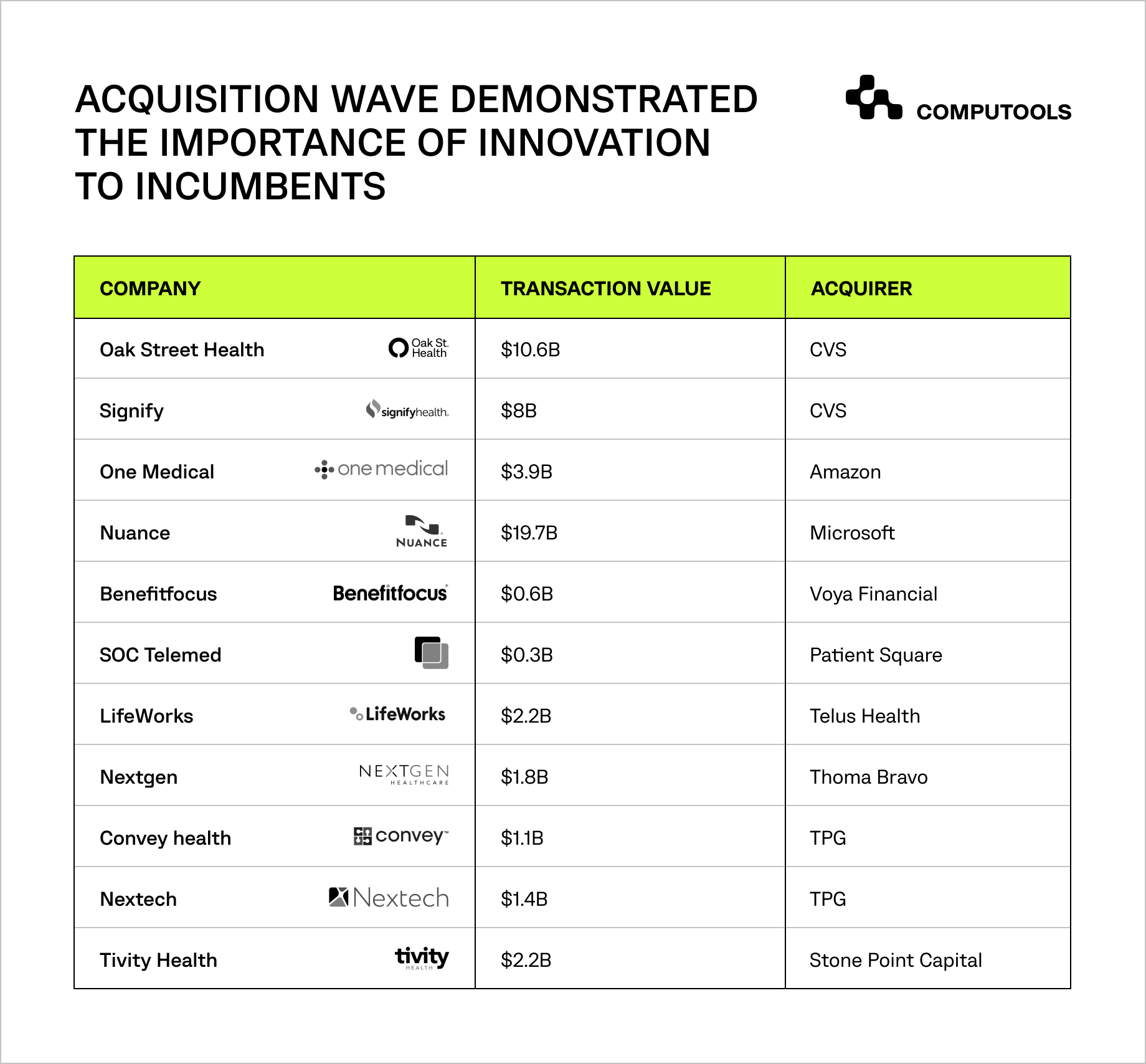
Would you want to discover which major corporations are currently making investments in medical software?
Companies from the US, Germany, and China regions are in the forefront of the investor firms. Because of this, large medical organizations and startups invest in the development of advanced healthcare technologies.
Investors view healthcare software as a goldmine as hospitals and clinics use it to enhance patient outcomes, maintain regulatory compliance, and increase data security.
In this blog post we will discuss the 20 most popular types of healthcare software in 2024 and 2025 to invest in or to develop.
Top 20 Healthcare Software You Need to Know About
Programs and Apps for Patients
1. Mobile Health Apps
These days, mHealth applications are an essential component of contemporary healthcare offerings. By streamlining administrative duties like paying medical bills, making appointments, and enabling virtual chats with nurses or physicians, these user-friendly apps empower patients.
Patients may easily access a variety of telehealth services with the help of effective mobile health applications, often serving as prime healthcare software examples in the industry.
These cutting-edge mHealth apps’ connection with EMR/EHR software systems is one of their most notable features. During a virtual consultation, medical practitioners can easily access relevant medical records with the required agreement from the patient.
This smooth information flow improves efficiency by facilitating quick data sharing for prescriptions, referrals, and other critical patient care components.
mHealth applications are a welcome disruption to the healthcare sector when they are skillfully incorporated with national or global healthcare infrastructure.
They redefine the ways in which patients access their healthcare, setting new standards for digital healthcare solutions, driven by advancements in HealthTech software development.
2. Health Tracking Apps
A health tracker is an electronic program designed to track and manage information related to healthy living and track progress. Using a health tracker allows to compile all data into a relevant picture of a person’s general lifestyle, whether or not it is healthy.
Additionally, it turns these figures from being a collection of arbitrary numbers into something more meaningful, giving them actual significance in our lives. Too often we track our activity and meals but don’t turn that data into healthy lifestyle decisions in ways that really matter.
Health trackers and smartphone applications, as part of broader medical software programs, provide behavior-change strategies that can lead to weight reduction and other health advantages, such as goal-setting, immediate feedback and rewards, and social variables like community sharing of success stories.
The data from a health tracker helps people better understand how leading a healthy lifestyle affects their appearance and mood, enabling them to make more educated decisions and, in the event that their current plan isn’t working for them, to develop a new strategy.
3. Medical Diaries
The Medical diaries go beyond typical health apps designed for maintaining a healthy lifestyle by specifically tracking illnesses and medical conditions. These programs allow patients to log symptoms, medications, and treatment progress, providing a detailed record of their health journey.
Medical diaries can integrate with physician or hospital clinical software, enabling seamless data sharing with healthcare providers for more informed decisions.
Alternatively, they can be stored locally on the patient’s device, giving individuals control over their health data while ensuring they have an accessible record of their condition for future consultations.
4. Medication Management Apps
When taking pharmaceuticals, patients of all ages and illnesses have difficulties include incorporating them into daily routines, comprehending the effects and side effects, and tracking results.
Given the fact that the majority of individuals own a smartphone, mobile applications provide a platform for such a customized assistance tool that is portable.
Medication management applications provide users with a number of advantages, including the ability to track medication dose and adherence, manage prescription refills, receive reminders when it’s time to take their meds, and access information about drugs, including possible interactions and dosing instructions.
These apps can also integrate with healthcare management software, ensuring a more streamlined approach to patient care and medication tracking.
Medical Systems for Facilities and Physicians
5. Electronic Health Records
An Electronic Health Record (EHR) is an electronic version of a patient’s medical history that is kept up to date by the healthcare provider. It may contain all of the important administrative and clinical information, such as demographics, problem notes, and medication information, that is pertinent to the patient’s care under a specific provider.
Data is captured by electronic health records for risk management, utilization reviews, resource planning, and continuous quality improvement, but not usually for human resources.
When creating guidelines for EHR use, privacy, treatment expenses, and patient quality of life must all be balanced. In contrast, an electronic health record offers a more comprehensive, long-term picture of a patient’s health as it aggregates patient information from many physicians and practices, often integrating with healthcare software systems.
It covers the patient’s demographics, test findings, medical history, history of present disease, and medicines.
For example, the EHR can enhance patient care by reducing the frequency of medical errors, cutting down on redundant testing, shortening treatment wait times, and empowering patients with knowledge to make wiser decisions through the use of patient software programs that give them greater control over their health data.
6. Clinical Decision Support System
Its goal is to support medical professionals in the analysis of patient data, enabling them to use that knowledge to make diagnoses and create treatment plans. Clinical decision support helps guide decisions regarding a patient’s treatment by providing timely information, typically at the point of care.
Clinical teams benefit from CDS tools and systems by having some mundane chores taken care of, possible issues flagged, or recommendations for the patient and clinical team to think about, all of which rely on effective healthcare software.
These medical software systems enhance the accuracy and efficiency of clinical decision-making, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
7. Medical Diagnosis Software
Advanced tools and a worldwide knowledge base are provided by medical diagnosis software to help with prompt and accurate diagnosis. This program does more than just keep medical records. It uses artificial intelligence (AI) to evaluate massive volumes of data, including securely exchanged anonymised patient records across healthcare providers.
This enables medical professionals to close any informational gaps, which may result in a more comprehensive assessment of a patient’s health. Certain applications for medical diagnostics even allow users to examine their symptoms and determine whether a trip to the doctor is required.
Moreover, medical software for doctors often integrates seamlessly with software used in hospitals.
8. e-Prescribing Software
Government rules can cause variations in e-prescription software across different countries. The fundamental principle, however, remains unchanged.
Doctors may generate new prescriptions, track their histories, renew them, or cancel them as needed with the use of e-prescribing software. In some countries, you may easily call the pharmacy of your choosing using the program.
All things considered, the E-prescription software program improves patient and doctor safety and security, saves time, and enables medical personnel to check for drug conflicts with previously consumed medications.
Advancements in healthcare software development continue to enhance the functionality and security of these e-prescribing systems, making them even more effective for both patients and healthcare providers.
Specialized Healthcare Systems
9. Telemedicine Software
Telemedicine software connects patients with doctors via video conferencing or secure messaging systems. This opens up a world of possibilities, making healthcare more accessible to folks in rural areas, those with hectic schedules, or anybody who wants the ease of a virtual visit.
Creating telemedicine solutions entails providing patients with a customized health center where all of their information is properly arranged – name, age, medical history, the whole nine yards.
The program also has a convenient calendar that keeps track of all booked appointments, so patients never miss a visit. Finally, customers receive timely reminders about impending visits, ensuring that they are always prepared for their virtual checks.
These solutions represent various types of healthcare software and highlight the importance of medical computer programs in enhancing patient care and accessibility.
10. Medical Database Software
Medical database software allows professionals to access a continually updated encyclopedia with a few clicks. This sort of tool allows anybody to search for information by keyword, filter by diagnosis or treatment, and even produce reports to track trends and evaluate patient data.
Doctors may have years of experience, but an uncommon disease can still throw them off guard. That’s when this solution comes in helpful.
It’s an excellent resource for locals and students alike. These databases allow users to investigate certain illnesses, identify various treatment choices, and view real-world scenarios. A search bar and filters are only two examples of the minimalist design components that some medical database software uses to make information access and care management even more accessible.
For those who prefer a physical copy, downloadable healthcare records options can be available as well. This software illustrates the importance of medical software applications in enhancing clinical practices. Continuous healthcare software development also ensures that these tools remain relevant and effective
11. Medical Research Software
Doctors may examine enormous datasets, such as clinical trial findings, genetic data, and public health statistics, with the use of medical research software.
Advanced features that enable researchers to find trends, test theories, and eventually uncover new information about human health include data visualization tools and statistical analysis skills.
Medical software projects play a crucial role in developing these advanced features, enhancing researchers’ ability to analyze complex data.
By facilitating the global exchange of data and discoveries among medical professionals, research platforms expedite the creation of novel treatments and cures. Investigators may concentrate on the research rather than the software with the help of interactive dashboards that provide safe data-sharing choices, integrated collaboration tools for communication, and drag-and-drop functionality for investigating trends.
12. Medical Imaging Software
Basic X-rays were a long way behind medical imaging. These days, visualization software elevates the experience to a whole new level, particularly with regard to CT, PET, and MRI images. It enables for the construction of 3D models for printing bespoke medical equipment or even prostheses.
This may be used, for instance, by a dentist to create and print a three-dimensional model of a patient’s jaw before to intricate oral surgery.
Such software adjusts its design to suit the requirements of experts. In order to facilitate cooperation among healthcare practitioners, there should be safe image-sharing functions with access limits, sophisticated visualization features for in-depth analysis (such as 3D reconstruction or picture overlays), and user-friendly image acquisition tools for clear and consistent image collection.
13. Hospital Management Software
A Hospital Management System (HMS) manages the whole intake process, including collecting insurance information, monitoring vital signs, and even organizing lab testing. This saves time and decreases mistakes, allowing personnel to focus on what’s most important: providing exceptional patient care.
But the advantages go well beyond urgent medical attention. Patients may visit the appropriate physicians at the appropriate times by using an HMS to assist organize their appointments.
Moreover, this system is essential for software for hospitals and clinics, as it helps track inventories to keep the hospital stocked with the required supplies and drugs.
Additionally, this technology simplifies insurance claims and billing, which is a huge help to the finance department.
A feature of HMS design that provides real-time snapshots of important information including patient admissions, bed occupancy, and departmental performance is centralized dashboards.
Additionally, there could be certain modules that are customisable, enabling other departments (such pharmacy and billing) to customize workflows to meet their unique requirements.
14. Pharmacy Management Software
The pharmacy information system, often referred to as the pharmacy management system, is a system that facilitates and saves data in order to maintain and organize the medication usage process in pharmacies.
Pharmacy use only versions of these systems are possible, or in a hospital context, pharmacies can be incorporated into an inpatient computer physician order entry (CPOE) system.
Data entry and retention policies, security restrictions to safeguard patient health information, and a user interface are all essential for a basic, working pharmacy management system.
Computer software for pharmacies is either acquired pre-made or offered as a service by a drug distributor. Various pharmacy software operating systems are common place throughout the many practice settings.
15. Laboratory Information Management System
A software-based solution with capabilities to support the operations of a contemporary laboratory is called a laboratory information management system (LIMS), also sometimes called a laboratory management system (LMS) or laboratory information system (LIS).
Healthcare software providers offer these systems, which enable data monitoring and workflow, flexible design, and data interchange interfaces that support their use in regulated environments.
Over time, a LIMS’s functions and applications have expanded from basic sample monitoring to an enterprise resource planning tool that handles several facets of laboratory informatics.
Central to its operation, LIMS encompasses five key phases of laboratory processing, including sample reception, analytical workload management, data storage, and reporting, with a strong emphasis on sample management through barcoding and tracking mechanisms.
Moreover, modern LIMS increasingly integrates with laboratory instruments and applications, supports electronic data exchanges, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards, enhancing overall efficiency and data handling within laboratory environments.
This evolution reflects the broader trends in HealthTech software development, as laboratories seek to optimize their processes and improve patient outcomes.
Quality and Financial Management Support
16. Quality Management Systems
A quality management system (QMS) is an assemblage of company procedures designed to reliably satisfy customer needs and raise their level of satisfaction. It is connected with a medical facility’s mission and strategic direction (ISO 9001:2015).
It is defined as the objectives and ambitions of the hospital, together with the rules, procedures, recorded data, and resources required for its implementation and upkeep.
Hospital administration software includes quality management software that helps firms manage all product and quality records and documentation, including product specifications, work instructions, standard operating procedures (SOPs), quality policies, and training records, among other things, to satisfy highly regulated standards. It centralizes these papers’ storage.
Quality management software is used by businesses to ensure that they adhere to ISO, OSHA, FDA, and other industry standards and guidelines, hence reducing the risk of noncompliance.
17. Revenue Cycle Management
Healthcare systems throughout the globe employ revenue cycle management, or RCM, to track client revenue from the time of the patient’s first visit or interaction with the system until the patient’s last payment of any outstanding debt. It is a typical aspect of managing health care.
According to one definition, the revenue cycle includes “all clinical and administrative functions that contribute to the capture, management, and collection of patient service revenue.”
It is a cycle that goes through a typical healthcare interaction from admission (registration) to final payment (or adjustment off of accounts receivables) and depicts and explains the life cycle of a patient (and subsequent revenue and payments). Errors are decreased and prevented in a healthy healthcare revenue cycle.
18. Practice Management
One type of healthcare software that handles the daily operations of a medical practice, including veterinary practices, is called medical practice management software (PMS). Users of this program may often record patient details, make appointments, keep track of insurance payors, handle invoicing, and provide reports.
PMS and electronic medical record (EMR) systems are frequently linked. Although certain data from a PMS and an EMR are similar, including as provider and patient information, in general, the EMR system helps the practice with clinical issues, whilst the PMS is utilized for administrative and financial issues.
Different suppliers are frequently used by medical offices to supply PMS and EMR systems. One of the trickiest parts of the process is integrating the PMS and EMR software.
19. Compliance Management
A Compliance Management System in healthcare is a structured framework designed to ensure that healthcare organizations adhere to regulations, standards, and best practices. It includes policies, procedures, and monitoring mechanisms that help mitigate risks related to patient safety, data privacy, and financial accountability.
By implementing a robust compliance management system, healthcare providers can enhance patient trust, avoid legal penalties, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Regular training and audits are integral to this system, enabling organizations to identify potential compliance gaps and adapt to evolving regulatory requirements.
20. Patient Portal
A Patient Portal is a secure online platform that provides patients with convenient access to their personal health information and healthcare services. Through the portal, patients can view medical records, schedule appointments, request prescription refills, and communicate directly with their healthcare providers.
This tool enhances patient engagement by empowering individuals to manage their health proactively and access resources, including medical software for patients.
By facilitating better communication and information sharing, patient portals contribute to improved healthcare outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Expert companies have the necessary knowledge and experience to develop solutions that meet specific business needs. They can offer innovative ideas, optimize processes and ensure that the final product meets the highest quality standards.
Moreover, working with such professionals can significantly reduce development time and minimize the risks associated with the introduction of new technologies.
Your Partner in HealthTech Development
Choosing Computools for your health tech development means gaining access to rich expertise in the healthcare industry. Our software development company is committed to delivering solutions that focus on quality, efficiency, and saving time.
We adhere to international standards with our ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 27001:2013 certifications, ensuring that our processes meet the highest quality and information security benchmarks. Our team of professional engineers with niche skills can deliver innovative and customized solutions tailored to your unique needs.
With an established position in the local job market and international partnerships, we have the stability and resources to support your projects effectively. You can also gain insights from our case studies and our clients’ testimonials, showcasing the success we have achieved together.
Reach out to us at info@computools.com for personalized insights and support in your healthcare technology development path.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”