In enterprise operations, IoT (the Internet of Things) software integrates with critical business systems. Usually, these are ordering systems, robotics, scheduling, and more. Such software enhances task execution.
The C-level executives integrate it to reduce operational costs, collect and analyse data so that processes can be optimized and goals can be achieved.
All too often, what starts out as a simple task evolves into a number of IoT implementation challenges that must be overcome to reach the desired result.
IoT Software Implementation Challenges
According to an IDC report, the number of connected IoT devices worldwide will generate 75.4 zettabytes of data by 2025.
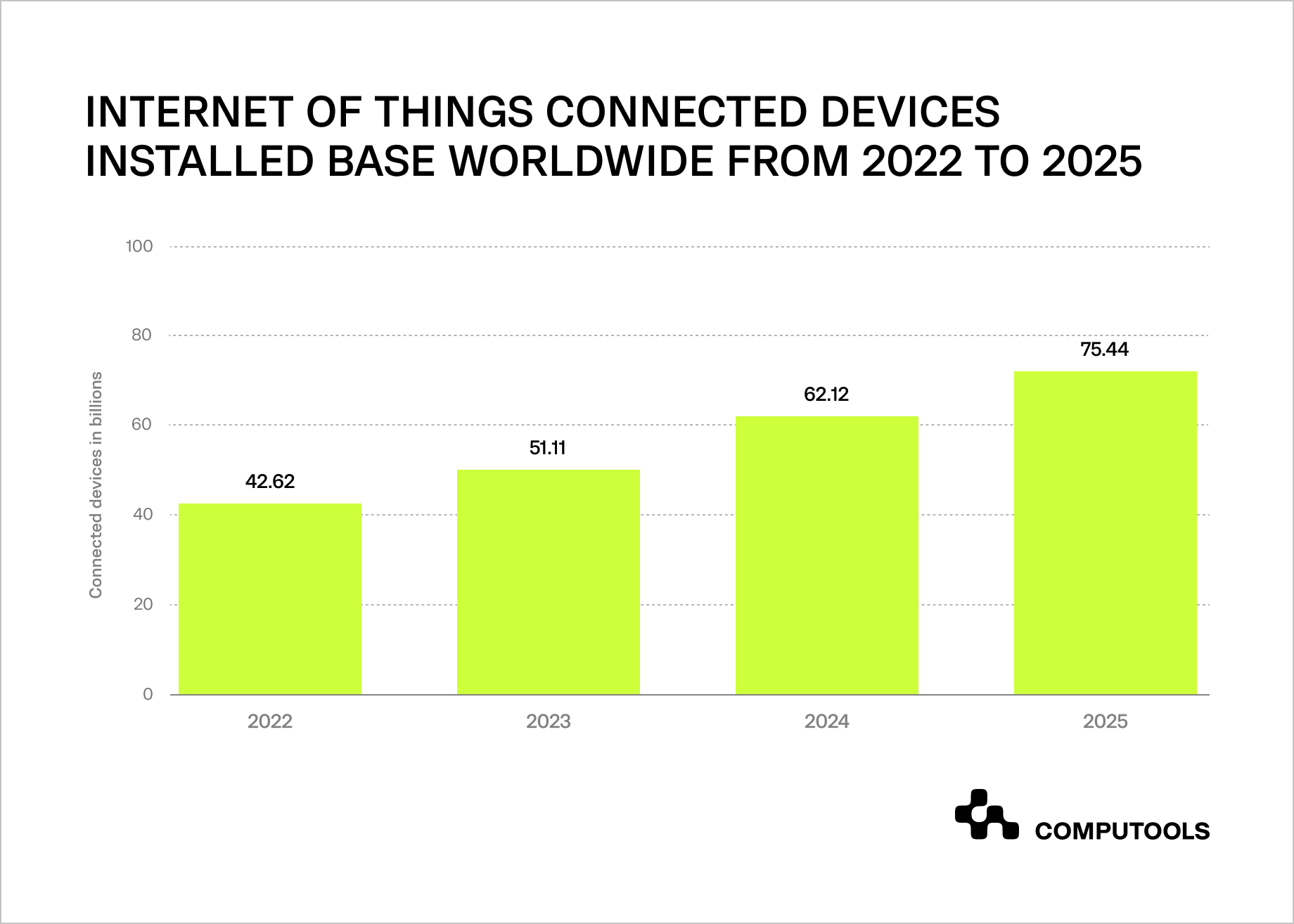
Additionally, a survey by Bain & Company found that 90% of executives believe IoT will significantly impact their industry, and 40% plan to implement IoT solutions within the next two years.
About 60% of enterprises are already implementing IoT, but only 30% are ready to say they’ve done so successfully. Most business executives cannot yet appreciate the value of implementing IoT software because its benefits don’t begin to bear fruit for some time after implementation.
By focusing on reducing operating costs, companies often miss out on IoT’s ability to solve consumer problems.
With the number of IoT devices expected to reach over 17 billion by 2033, consumer internet and media devices, like smartphones, represent the most significant use case for IoT devices in the consumer market.
By 2033, there will be over one billion IoT devices in use cases such as IT infrastructure, smart grid, asset tracking and monitoring, and linked (autonomous) cars.
We already know that IoT software impacts efficiency, customer satisfaction, and productivity in the long run, but the gap between understanding why to use IoT and the real value of putting it into practice is usually why enterprises are slow in adopting IoT software solutions.
They fear such risks as security, device complexity, and interoperability. Companies must address them to fully see the potential of this transformative technology.
1. Compatibility of Various IoT Systems
A main issue enterprises encounter is when they attempt to integrate the operations of their existing equipment with an entire system of embedded IoT sensors.
Companies need to involve various components such as hardware, software, and network protocols when implementing IoT software solutions. It needs to be done to ensure the effective functioning of the whole system.
It takes a lot of time to link and debug systems from different manufacturers in order to achieve a working interface. Integrating IoT software with older, existing systems to obtain reliable and necessary information will encounter many software conflicts.
You can install external sensors on devices, but that may be a temporary solution. However, here, the difficulty lies in the need to determine which particular sensor functions are the priority and how to use them.
2. Authentication and Identification
Today, the number of devices connected online amounts to tens of billions. Among the IoT implementation challenges is the precise and secure connection of each of them, which raises huge security concerns for enterprises across the U.S.
However, due to the high complexity of this task, many companies worry about the effectiveness of their devices along with their existing systems.
To connect all these IoT devices to a single platform, an entirely new system architecture is required to be responsible for authentication and identification.
3. Integration of IoT Points with IoT Software
The successful implementation of IoT software depends entirely on its integration with existing systems. Integrations that fall short on delivering what was expected or require complicated training to learn how to use will lead to negative outcomes: reduced productivity, poor customer service, failure to achieve KPIs, etc.
That is why the process of integration is such a critical component in an IoT project. Unfortunately, the difficulty lies in the need to connect a large number of sensors to the platform.
4. IoT Data Storage
Many companies leverage IoT devices to gather real-time data to facilitate business decision-making and boost customer satisfaction. However, all the collected data should be synthesized and transferred in a specific format to store on storage systems – which is prompting organizations to reconsider their data storage infrastructures. A company should store data generated from the Internet of Things, and this data is consistently growing.
Most IoT data (structured or unstructured) performs analytical functions to generate insights. The analyzed results have to be pushed back to a central terminal. This prompts demand for high-capacity and high-speed storage, as well as advanced memory processing technologies.
5. Connectivity and Power Management
Since the number of devices increases, so does the demand for effective power management. Specific IoT devices, such as printers, can utilise AC power while being placed in accessible locations.
In contrast, others are wireless and can be situated in remote areas where battery power is the only option. Despite advancements in storage technology, battery life remains a persistent challenge for IoT networks.
Enterprises should consistently monitor when an IoT device’s battery requires recharging or replacement. Therefore, it is crucial to identify devices that conserve power when not in use to ensure efficient power management.
Although some devices can be powered via a LAN cable, this method is only suitable for those that require minimal power.
Correct power distribution is another factor. This ensures that as many devices as possible will have access to a network, instead of working autonomously from batteries. If a device is stationed in a difficult place to access, battery replacements can be extremely problematic.
A stable and high-speed internet connection is required to obtain reliable and timely information from IoT sensors. This is especially critical for companies involved in all types of transportation and delivery.
Nevertheless, any remote operations will require additional equipment on the premises of warehouses to improve the quality of signals collected by sensors and transmitted across networks via routers or LAN, MAN, and WAN connections.
Companies will also be responsible for establishing and maintaining high-speed connections between these networks, as well as managing the growing number of devices being connected to them.
6. Unstructured Data Processing
The introduction of countless additional sensors means processing enormous volumes of unstructured information.
IoT software needs to be effectively configured and deployed to organize, analyze, and filter out the most useful data. Moreover, unstructured data is difficult to store and use for future analysis.
The combination of IoT and Big Data temporarily solves this problem by speeding up the analytical process.
However, Big Data itself is also massive, which adds challenges to IoT software development. The need to integrate IoT solutions with Big Data tools is a long process being undertaken by some of the biggest tech companies.
7. Incorrect Data Capture
If we were to assume a situation where all previous IoT adoption barriers had been resolved and a stable system had been brought to market, incorrect data collection would still plague the process.
This is because systems record absolutely everything: any anomalies, unwanted incidents, or failures of IoT software.
The inclusion of such information in analytical data can adversely affect decision-making, which subsequently affects consumers and the company collecting it.
8. IoT Data Analytics
The real value of an IoT solution is in generating effective insights obtained from the collected IoT data. This requires a high-performance analytical platform with tools capable of processing huge amounts of data.
Moreover, the implementation of IoT software introduces new obstacles such as data volumes increasing to astronomical levels, causing the need for IoT analytics to diverge further from traditional analytics.
The real-time nature of IoT data forces analytics to happen in real time so that companies can benefit from this type of data collection.
Time series data is another issue that refers to any data with a timestamp. The challenge here is that most conventional databases are not equipped to handle these huge volumes of time series data.
9. Data Security
In 2024 the number of cyberattacks progresses. Businesses shout out more and more IoT challenges and issues.
According to Microsoft research, about 25% of IoT devices will be susceptible to attacks by hackers in the coming years.
Large corporations are the most vulnerable to data leakage. However, hacking can occur both from the side of the corporation as well as from the side of the consumer.
IoT software companies are responsible for solutions that provide enhanced security on both ends. Thus, they must consider all possible angles of attack, including protecting users from themselves.
This begins with simple procedures such as prompting users to change their default password.
10. Cost Efficiency
IoT infrastructure can be costly, and the expenses associated with maintenance, updates, device replacements, and technical expertise can quickly go up.
As the technology continues to advance, finding the right team with the required expertise can be challenging, but businesses keep investing in IoT, which leads to infrastructure catching up with the technology.
11. Developers’ Skill Set
It is still challenging to find high-profile experts with diverse skills, including IoT, security, hardware, and user requirements. Such expertise often demands further specialization in the industry.
A supply-demand mismatch has arisen due to the IoT industry’s continued growth and the rising need for qualified workers.
As a consequence, project prices increase, and it might be difficult to recruit experts with the necessary skill set to complete a project.
12. Customer Satisfaction
Among the IoT challenges and solutions, bringing value to consumers ranks highest. Companies striving to get the most from IoT technology must clearly define what value they intend to receive.
Due to an incorrectly thought-out strategy affecting customer satisfaction, an IoT value proposition should consider the business and operational value of a product or service and its impact on the customer.
For example, deciding to replace live operators with custom software solutions is a serious step. Before doing so, a company must focus on how the user experience will change. And make changes to guarantee that high-quality assistance persists.
The most common mistakes usually occur when implementing ill-conceived UX solutions, weak strategies, and weak transitional processes. That is why a holistic UX approach focused on improving comfort and value for the consumer is a must.
Therefore, most enterprises turn to professional companies for consultation in developing full-cycle IoT solutions consisting of sensors, a network, and software. However, optimizing and improving an existing system also often requires outside help.
13. Job Displacement
Job displacement represents a significant challenge in IoT implementation as of 2024. While the technology can enhance operational efficiency and it also presents opportunities for economic growth, it simultaneously threatens traditional job roles.
To navigate this challenge successfully, stakeholders must prioritize reskilling, workforce adaptation, and responsible deployment of IoT technologies to ensure sustained employment opportunities amid technological advancements.
Of course, the IoT sector hasn’t peaked yet, so keep that in mind. There still has the potential for more automation. But the patterns seem to suggest that even if more jobs are gone, other ones will presumably take their place.
Based on empirical research, there is a positive correlation between IoT usage and increased employment in markets with a high density of IoT connections.
Additionally, a vast array of commercial and industrial uses that are frequently disregarded account for the majority of the potential benefits made possible by IoT.
IoT technology is presently being used in many different applications, such as automated warehouses and healthcare sensors. IoT adoption and productivity growth are positively correlated in all nations.
Let’s consider a number of ICT and economic factors that influence IoT adoption as well as employment results, such as GDP, human capital, and fixed and mobile broadband connections.
In all of the nations in the collection, there is no significant relationship found between IoT adoption and the unemployment rate or overall employment.
Nonetheless, given the huge differences in IoT adoption rates across OECD and non-OECD countries, a comparative analysis is more worthwhile. We may conclude that, with employment in the service sector driving this relationship, there is a significant and positive association between IoT adoption and overall employment in OECD nations.
14. IoT Business Potential
Merging ioT and manufacturing has enormous potential to optimise resource management, servicing, and asset monitoring in previously unheard-of ways. Proactive maintenance tactics, which avoid production outages and guarantee seamless supply chain operations, are propelled by the Internet of Things.
In particular, how can the relationship between proprietary and ageing industrial assets and information technology be efficiently established? This dispels the myth that IoT deployment requires only new construction, which is rarely practical. It is frequently seen as the main difficulty.
Business executives become skeptical of the IoT’s actual business potential as a result of these complications. Furthermore, the growth of linked devices raises asset diversity, volume, and complexity as the IoT ecosystem grows.
Managing several IoT technologies at once presents further difficulties. Even if the goal of IoT adoption is to link more assets, obstacles exist in achieving precise real-time localization.
Collaboration is therefore essential to overcoming these obstacles and solving asset management issues. You may establish a co-creation space that blends technological know-how and industrial knowledge by forming strategic alliances with ecosystem participants.
Working with a company that provides expert IoT application development services is one approach to overcoming this barrier.
IoT technology Forecast
Experts think that 2024 will be a promising year for IoT technology. The demand for IoT development services is rising. We expect significant progress in the use of IoT software for industries such as Healthcare, Manufacturing, Logistics, and the construction of smart objects (smart homes, smart offices).
With the implementation of AI (ML) algorithms, IoT solutions will become more efficient and reliable. Moreover, cloud computing and SaaS solutions will make IoT more scalable.
Eventually, if businesses use IoT development services, they can leverage the power of connected devices for all their plans.
Energy consumption is one issue that businesses run with as they add more sensors. New IoT sensors, both external and internal, are becoming more modern as their use reduces energy expenditures by 5-12%.
However, the only challenge is in phasing out old sensors and replacing them with new ones. In the case of using old equipment, entire systems may require replacing.
Several companies are actively developing 5G wireless networks. Although the expected date for the introduction of this technology isn’t yet known, large-scale tests will commence this year. This new network protocol will be able to solve the problem of implementing IoT for enterprises operating remotely.
It is only a matter of time before the challenges of implementing IoT software and solutions will be resolved. In a period of constant invention and a continuously changing landscape of new solutions and innovations, companies will be looking for a solution that not only brings their processes into the modern age but future-proofs them against modern dangers as well.
IoT technology is constantly developing. Please feel free to contact Computools’s experts at info@computools.com to learn how IoT solutions can benefit your business.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”