MORE EFFICIENT FARM OPERATIONS
Achieved through smart automation, real-time livestock tracking, and AI-driven health and yield analytics built into custom farm management systems.
REDUCTION IN OPERATIONAL COSTS
Enabled by predictive planning, automated reporting, and centralized herd and resource management tools.
EXPERTS ON BOARD
100% of our agriculture clients partner with us long-term to scale innovation, improve productivity, and drive digital transformation in livestock operations.
AGRITECH PROJECTS DELIVERED GLOBALLY
From large-scale herd management platforms to IoT-powered farm apps, we build livestock software trusted by agribusinesses and AgTech innovators worldwide.
AI-Powered Livestock Health Monitoring System
We offer a customized animal health monitoring system using artificial intelligence, which integrates wearable IoT sensors (tracking key indicators such as body temperature, heart rate, activity, and chewing) with cloud analytics and machine learning. The system continuously evaluates health data and alerts farmers to anomalies that may indicate early signs of illness, infection, or stress.
Using the AI Feed Optimization System
With a custom-built feed optimization system, you can leverage real-time data from feeding systems, animal health metrics, and environmental sensors to create precise, cost-effective rations. By analyzing consumption patterns, weight gain, and feed composition, the system delivers tailored recommendations that boost efficiency and animal well-being. Integrated with smart feeders, it automates distribution, monitors inventory, and forecasts feed demand based on seasonal and market trends. A unified mobile and desktop dashboard gives farm managers full visibility and control, supported by built-in analytics for strategic feed budgeting. This solution helps you cut waste, lower feed costs, and improve livestock performance – every season.
IoT-Enabled Environmental & Safety Monitoring System
This solution leverages sensors and IoT devices to monitor environmental conditions, track animal health, and ensure consistent adherence to safety protocols across the farm. The platform provides predictive analytics, offering early alerts for potential safety risks to prevent accidents before they occur. Fully customizable to meet local regulations, the system automates compliance reporting, reducing the administrative burden. Additionally, it includes worker health monitoring features, enabling managers to track employee well-being and take proactive measures to ensure a safe and healthy workplace.
IoT-Driven Environmental Optimization & Sustainability Platform
This solution integrates IoT sensors with AI-powered analytics to provide real-time monitoring of water usage, waste management, and emissions. The platform helps farmers optimize resource consumption, reduce water usage, minimize waste, and lower the carbon footprint of farming operations. With predictive analytics for feed sourcing, farmers can make informed decisions to ensure sustainable and efficient feed supply chains. Additionally, the system offers detailed environmental performance reports, supporting compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability certification requirements.
Blockchain-Based Livestock Traceability Platform
This solution creates a robust digital traceability system that uses blockchain technology and IoT sensors to track the entire supply chain of livestock products. From the moment an animal enters the system, the platform records data on its origin, health status, feed consumption, transportation, and processing stages. Each transaction or movement is securely logged on the blockchain, ensuring full transparency, accountability, and real-time visibility across the supply chain. The platform seamlessly integrates with existing farm management software, providing real-time analytics and insights into each product’s journey from farm to table. Additionally, it ensures regulatory compliance by storing all required records in an easily accessible digital format, helping farmers and businesses maintain adherence to industry standards.
Intelligent Feed Management Software
With custom-built feed management software, you can take full control of your livestock feeding operations through real-time monitoring, AI-driven insights, and seamless automation. The system tracks feed consumption, integrates with nutrient requirement databases, and provides intelligent formulation recommendations based on species, age, health, and performance history. It also features inventory tracking, spoilage alerts, and predictive tools for seasonal planning and procurement. By connecting with IoT-enabled storage sensors and feeding systems, it ensures a continuous data flow and precise rationing—helping you minimize waste, reduce costs, and optimize animal nutrition across your farm.
Custom Smart Water Management System (SWMS)
A Smart Water Management System (SWMS) designed for livestock farms automates water delivery, monitors quality, and detects leaks in real time. By integrating IoT-enabled dispensers, sensors, and analytics, SWMS helps you optimize water usage, prevent waste, and ensure consistent hydration for your animals. With forecasting tools and automated adjustments based on weather and animal needs, the system improves both animal health and operational sustainability.
With a custom-built Farm Workforce Management Platform combined with automation tools for livestock operations. It includes digital scheduling, role-based task assignment, and automated checklists. The platform integrates with sensors and smart equipment, reducing manual labor for feeding, health monitoring, and environmental control. We also provide built-in training modules and dashboards that help managers identify skill gaps and measure employee performance. By minimizing repetitive tasks through automation and optimizing workforce deployment, farms can maintain high output levels despite staffing constraints.
Custom Environmental Waste Management System (EWMS)
An Environmental Waste Management System (EWMS) helps livestock farms monitor, manage, and report waste more efficiently. By integrating IoT sensors, runoff monitoring, and air quality tracking, EWMS ensures real-time oversight of waste storage and environmental impact. The system automates compliance reporting, issues alerts for threshold breaches, and supports nutrient recycling through smart manure application planning—helping you stay compliant, protect the environment, and turn waste into a valuable resource.
Using comprehensive Farm Management Software (FMS) that integrates data from various sources (IoT sensors, equipment, inventory management, weather forecasts), you can create a unified platform. This system enables real-time tracking and analysis of key farm metrics such as animal health, feed consumption, water usage, and environmental conditions. With predictive analytics, our platform suggests optimal actions based on current conditions, enabling farm managers to make more informed, data-driven decisions. The system also features customizable dashboards to visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) and provide detailed reports for stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
Custom Livestock Transportation Management System (LTMS)
A Livestock Transportation Management System (LTMS) enables real-time tracking of transport routes, automated delay response, and intelligent route optimization. By integrating with suppliers, warehouses, and carriers, LTMS streamlines collaboration and ensures efficient product movement. Advanced analytics help forecast market demand and adjust supply chain activities, preventing overstocking or shortages. The system also supports global trade compliance monitoring, reducing risks associated with regulatory delays and disruptions.
Mobile Workforce Training & Performance Management Platforms
Deploying mobile-enabled systems for workforce training and performance management empowers employees to improve their skills in modern farming practices through on-the-job learning, real-time feedback, and gamified engagement. These platforms enhance motivation and knowledge retention while promoting continuous upskilling. Integrated with HR and payroll systems, the solution automates workforce scheduling, monitors employee performance, and optimizes staffing levels — ensuring your operation is always equipped with the right number of skilled workers.
AI-Powered Livestock Health Monitoring System
We offer a customized animal health monitoring system using artificial intelligence, which integrates wearable IoT sensors (tracking key indicators such as body temperature, heart rate, activity, and chewing) with cloud analytics and machine learning. The system continuously evaluates health data and alerts farmers to anomalies that may indicate early signs of illness, infection, or stress.
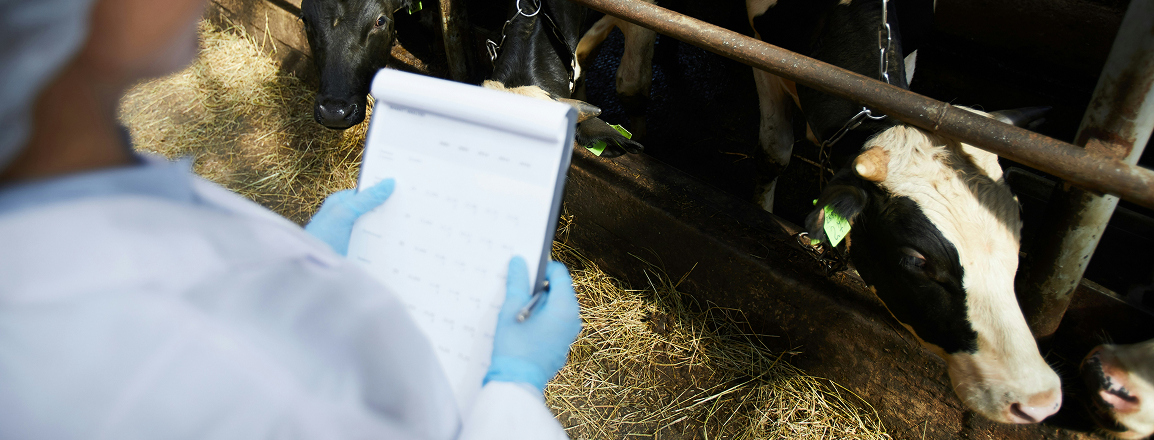

Using the AI Feed Optimization System
With a custom-built feed optimization system, you can leverage real-time data from feeding systems, animal health metrics, and environmental sensors to create precise, cost-effective rations. By analyzing consumption patterns, weight gain, and feed composition, the system delivers tailored recommendations that boost efficiency and animal well-being. Integrated with smart feeders, it automates distribution, monitors inventory, and forecasts feed demand based on seasonal and market trends. A unified mobile and desktop dashboard gives farm managers full visibility and control, supported by built-in analytics for strategic feed budgeting. This solution helps you cut waste, lower feed costs, and improve livestock performance – every season.
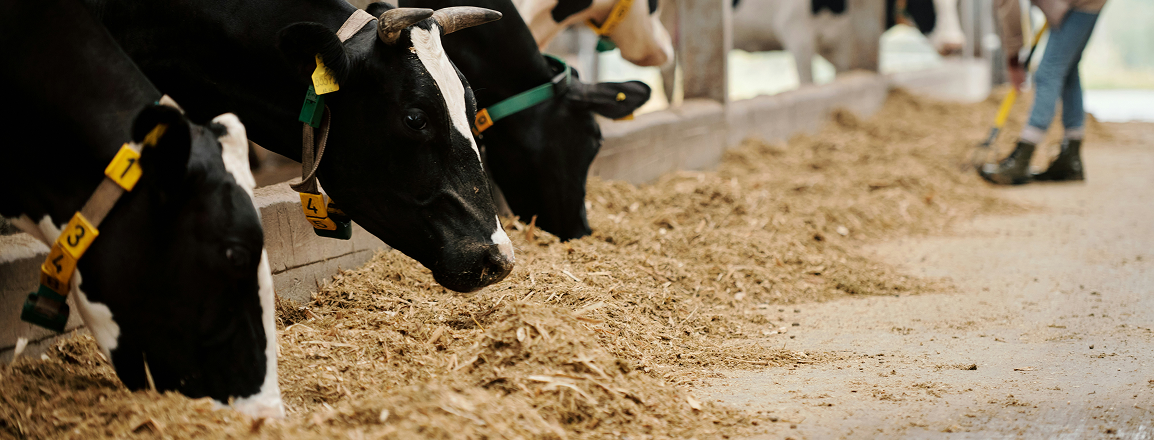

IoT-Enabled Environmental & Safety Monitoring System
This solution leverages sensors and IoT devices to monitor environmental conditions, track animal health, and ensure consistent adherence to safety protocols across the farm. The platform provides predictive analytics, offering early alerts for potential safety risks to prevent accidents before they occur. Fully customizable to meet local regulations, the system automates compliance reporting, reducing the administrative burden. Additionally, it includes worker health monitoring features, enabling managers to track employee well-being and take proactive measures to ensure a safe and healthy workplace.
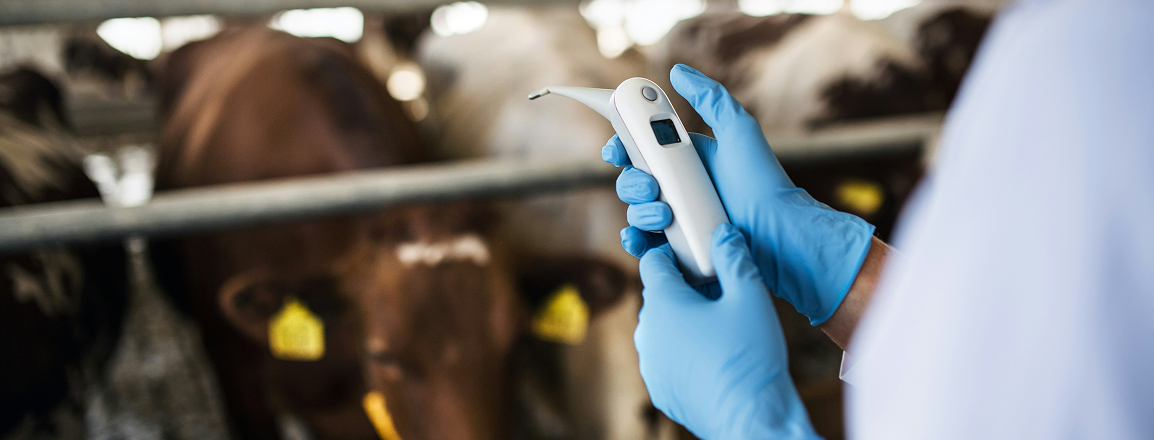

IoT-Driven Environmental Optimization & Sustainability Platform
This solution integrates IoT sensors with AI-powered analytics to provide real-time monitoring of water usage, waste management, and emissions. The platform helps farmers optimize resource consumption, reduce water usage, minimize waste, and lower the carbon footprint of farming operations. With predictive analytics for feed sourcing, farmers can make informed decisions to ensure sustainable and efficient feed supply chains. Additionally, the system offers detailed environmental performance reports, supporting compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability certification requirements.

Blockchain-Based Livestock Traceability Platform
This solution creates a robust digital traceability system that uses blockchain technology and IoT sensors to track the entire supply chain of livestock products. From the moment an animal enters the system, the platform records data on its origin, health status, feed consumption, transportation, and processing stages. Each transaction or movement is securely logged on the blockchain, ensuring full transparency, accountability, and real-time visibility across the supply chain. The platform seamlessly integrates with existing farm management software, providing real-time analytics and insights into each product’s journey from farm to table. Additionally, it ensures regulatory compliance by storing all required records in an easily accessible digital format, helping farmers and businesses maintain adherence to industry standards.
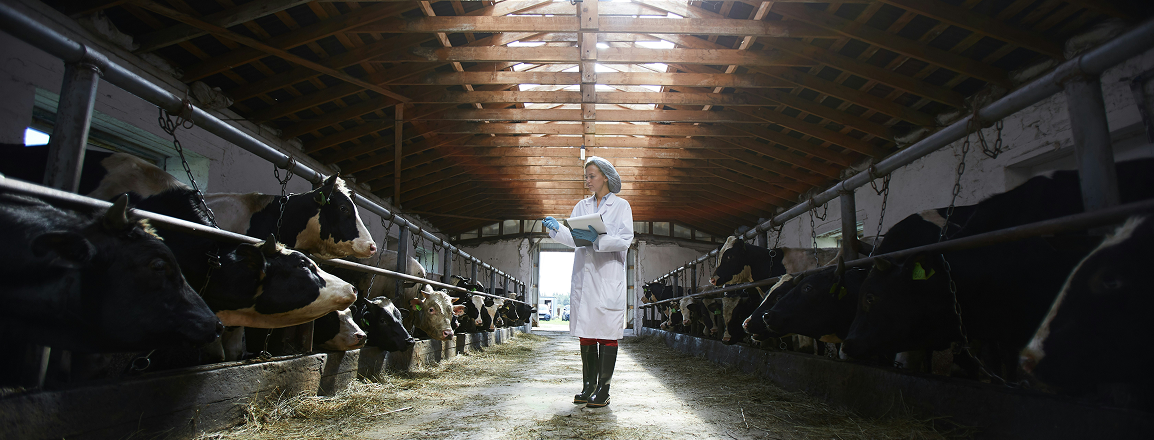

Intelligent Feed Management Software
With custom-built feed management software, you can take full control of your livestock feeding operations through real-time monitoring, AI-driven insights, and seamless automation. The system tracks feed consumption, integrates with nutrient requirement databases, and provides intelligent formulation recommendations based on species, age, health, and performance history. It also features inventory tracking, spoilage alerts, and predictive tools for seasonal planning and procurement. By connecting with IoT-enabled storage sensors and feeding systems, it ensures a continuous data flow and precise rationing—helping you minimize waste, reduce costs, and optimize animal nutrition across your farm.

Custom Smart Water Management System (SWMS)
A Smart Water Management System (SWMS) designed for livestock farms automates water delivery, monitors quality, and detects leaks in real time. By integrating IoT-enabled dispensers, sensors, and analytics, SWMS helps you optimize water usage, prevent waste, and ensure consistent hydration for your animals. With forecasting tools and automated adjustments based on weather and animal needs, the system improves both animal health and operational sustainability.

With a custom-built Farm Workforce Management Platform combined with automation tools for livestock operations. It includes digital scheduling, role-based task assignment, and automated checklists. The platform integrates with sensors and smart equipment, reducing manual labor for feeding, health monitoring, and environmental control. We also provide built-in training modules and dashboards that help managers identify skill gaps and measure employee performance. By minimizing repetitive tasks through automation and optimizing workforce deployment, farms can maintain high output levels despite staffing constraints.

Custom Environmental Waste Management System (EWMS)
An Environmental Waste Management System (EWMS) helps livestock farms monitor, manage, and report waste more efficiently. By integrating IoT sensors, runoff monitoring, and air quality tracking, EWMS ensures real-time oversight of waste storage and environmental impact. The system automates compliance reporting, issues alerts for threshold breaches, and supports nutrient recycling through smart manure application planning—helping you stay compliant, protect the environment, and turn waste into a valuable resource.

Using comprehensive Farm Management Software (FMS) that integrates data from various sources (IoT sensors, equipment, inventory management, weather forecasts), you can create a unified platform. This system enables real-time tracking and analysis of key farm metrics such as animal health, feed consumption, water usage, and environmental conditions. With predictive analytics, our platform suggests optimal actions based on current conditions, enabling farm managers to make more informed, data-driven decisions. The system also features customizable dashboards to visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) and provide detailed reports for stakeholders and regulatory bodies.

Custom Livestock Transportation Management System (LTMS)
A Livestock Transportation Management System (LTMS) enables real-time tracking of transport routes, automated delay response, and intelligent route optimization. By integrating with suppliers, warehouses, and carriers, LTMS streamlines collaboration and ensures efficient product movement. Advanced analytics help forecast market demand and adjust supply chain activities, preventing overstocking or shortages. The system also supports global trade compliance monitoring, reducing risks associated with regulatory delays and disruptions.

Mobile Workforce Training & Performance Management Platforms
Deploying mobile-enabled systems for workforce training and performance management empowers employees to improve their skills in modern farming practices through on-the-job learning, real-time feedback, and gamified engagement. These platforms enhance motivation and knowledge retention while promoting continuous upskilling. Integrated with HR and payroll systems, the solution automates workforce scheduling, monitors employee performance, and optimizes staffing levels — ensuring your operation is always equipped with the right number of skilled workers.

Chief Delivery Officer

We develop software integrated with RFID, GPS, and QR tagging technologies to track individual animals in real time, providing full visibility into location, movement, and ownership history across farms and supply chains.
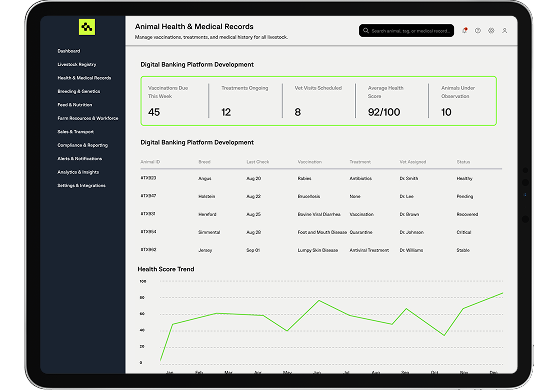
Computools builds secure platforms for storing and managing health records, vaccination schedules, and veterinary treatments, helping farms ensure animal welfare, reduce disease risks, and stay compliant with regulations.
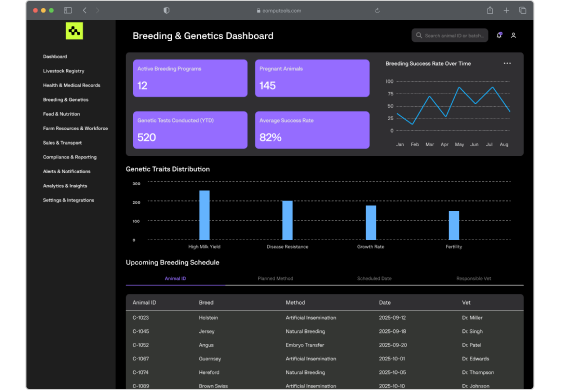
We create data-driven tools to manage breeding cycles, genetic lineage, insemination tracking, and reproduction performance, maximizing herd quality and productivity through science-backed planning.
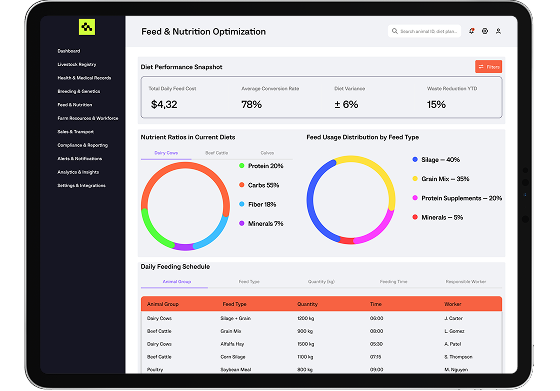
Our software solutions help track feed inventory, automate ration planning, and monitor nutritional performance, reducing waste and ensuring optimal growth, yield, and feed conversion rates.
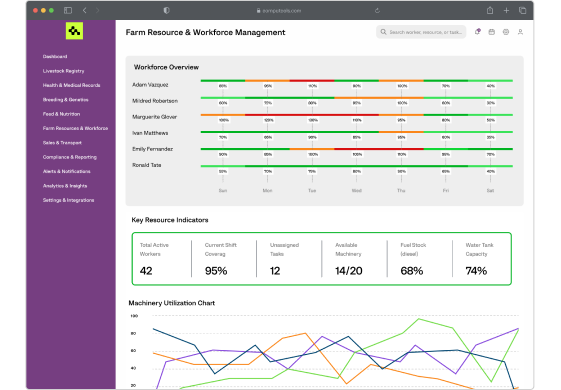
We build comprehensive platforms that manage farm operations, labor scheduling, task tracking, and equipment usage, streamlining resource allocation and improving overall productivity.
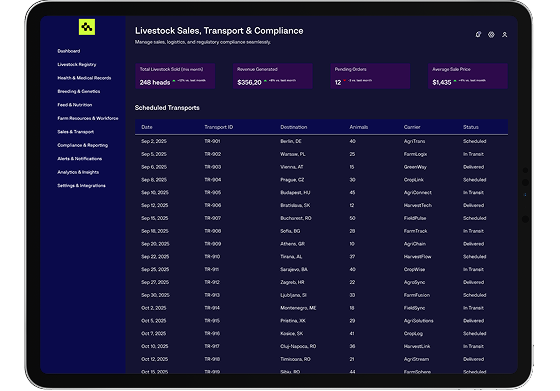
Computools delivers systems that handle livestock sales, transport documentation, compliance with animal movement regulations, and digital traceability, ensuring secure, transparent transactions and legal readiness.
“The team was very friendly and had the highest level of competence, engagement, and project management.”

“Computools predicted all possible points of our business growth and implemented them into the project.”

“We were highly satisfied with their deep understanding of our fintech processes and their project management was really superb.”

“Computools is a highly professional company with a skilled and responsive team. Their ability to propose valuable improvements and their dedication to the project made a significant difference.”

“The most noteworthy value that stood out was their exceptional experience in developing AI software solutions.”

“We were deeply impressed with their technical expertise, transparency, and flexibility. The team was highly skilled, easy to work with, and always proactive in solving challenges.“

“Computools offered non-standard solutions and maximized their investment in our business success.“

“Our company is impressed by their client-first approach and deep niche expertise.”

“A very comfortable collaboration and clear communication on every stage of platform development and maintenance.”

“After all these years, Computools never fails to arrive on time and with a quality that never ceases to amaze me. They work well as a team and are adaptable and communicative.”

“Within the first three months of its use, the designed program by Computools significantly reduced meter reading fraud by over 30%. Additionally, we saw a rise in operational effectiveness. Customer comments highlighted greater billing transparency and speedier service delivery, which contributed to an improvement in customer satisfaction levels.”

“They were professional, adapted to our short-notice needs, documented everything, and were transparent.”

“Thanks to Computools, we have seen a 15% growth in sales and a 40% boost in user satisfaction. Our image management has become more efficient, and our diagnostic capabilities have improved. Overall, the team has delivered a high-quality solution that meets our requirements.”

“Computools has significantly improved our LMS. The team holds regular meetings and provides detailed project reports, keeping us well-informed. We communicate via email, and overall, everything has gone smoothly.”

“Computools worked closely with us to understand our challenges. They developed a platform that integrated seamlessly with our existing infrastructure and Automatic Identification Systems (AIS) to capture private vessel data.”

“Computools’ work has had a positive impact on the client’s business. The team is flexible and responsive to the client’s needs. Their expertise has been key to the project’s success. Overall, the engagement has been positive.”

“Due to the platform’s use, the new products’ generated go-to-market timeline improves by 20%, cutting down on plan costs and, most importantly, enhancing the connection between the departments. The availability of near real-time information and the enhancement of the speed of decision-making are truly remarkable.”

“Thanks to Computools, we have successfully implemented our system and reduced the need for manual inspections. The team works in regular sprints and keeps us updated on progress. Their personalized approach, ability to listen, adapt, and continuously refine their methods are truly impressive.”

“Computools’ team truly impressed us with their dedication to the project, their ability to adapt to our processes, and their exceptional hard skills. This allowed us to identify many risks in the initial development stages and address some gaps in our processes. Professionalism, contribution, and flexibility are what define Computools. Based on my experience, I strongly recommend Computools for Dedicated Delivery and outsourcing project services!”

“Computools has delivered a functional solution that helped us increase revenue fivefold, reduce costs, and boost productivity. The team efficiently manages tasks in Jira and keeps us updated through weekly calls. Their productive approach and strong work ethic truly stand out.”

“Computools’ technical knowledge is impressive.They delivered the product on time, within the agreed budget, and fully aligned with our requirements.”

“Thanks to Computools’ efforts, we have seen compliance with deadlines and budget and team scalability as needed. The team has a confident project manager who delivers a professional and organized project. Moreover, Computools has quickly onboarded to the project and delivered fast results.”

“Thanks to the new solution, we’ve significantly reduced manual marketing workflows. Computools manages the project effectively, using Scrum methodology to execute tasks efficiently. Their problem-solving skills and ability to anticipate challenges set them apart from other providers.”

“Computools has successfully delivered everything as planned, adding value to the app. The team is highly approachable, tracks progress, and provides real-time updates via Slack. They maintain smooth communication through email and messaging apps, regardless of time zones.”

“Thanks to Computools, we now have an app that integrates 2,000 users into a single platform, significantly reducing the time spent on data exchange between systems and applications. The team manages our collaboration effectively and quickly adapts to changes. Overall, our experience has been highly successful.”

“Computools has been responsible for creating a novel database and front-end solution, incorporating both the development portal for digital standards and a modern shop for the sale of these standards. Throughout the course of the project, we have been consistently impressed by the professionalism exhibited by the Computools team, as well as their detailed understanding of our client’s processes. Their expertise, commitment to our objectives, and consistent delivery of high-quality work are notable aspects of their service.”

“Thanks to Computools, the client saw a 35% increase in daily active users and a 25% rise in user retention rates. The Android app also saw a 20% reduction in load times. User feedback indicated high user satisfaction; the feedback highlighted the product’s enhanced navigation and content linkage.”

“They are some of the best software developers I ever had the privilege to work with. Among other skills, their project scope and time estimation are very good and when wrong will work around the clock to make the date especially if it has business consequences. Not only are they amazing software developers, but they are also great people to work with. I am in awe seeing their devotion.”

“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”

“After analyzing our requirements, Computools outlined potential solutions and deadlines for each stage. They designed the user flows and defined the user personas. They built the platform infrastructure and oversaw its implementation. Once we finished development, we conducted usability tests to assess their submitted work. Computools led an organized, agile team that adapted to our evolving needs. They listened to our feedback and managed their time well throughout the project.”

“The application perfectly meets the large-scale demands of the project, with the team creating an effective solution that works well and provides the required level of control. They were communicative, responsive, and proactive throughout the project, demonstrating their experience at all times.”
“The Computools team came to us with ideas, and that’s unusual. I’m satisfied that they gave us the right recommendations which are contemporary and relevant for today’s users. Because with other companies on previous projects, it was like pulling teeth to get them to make suggestions. The product received positive feedback even before being implemented and has led to significant customer and revenue growth.”

“We had to meet a significant increase in the development, so we needed to scale up relatively quickly but cost-effectively. The result definitely meets our expectations. The completed project received positive feedback for features and overall design. They’re very organized from a project management perspective and they’re technically competent. We appreciated their innovativeness, professionalism, and great communication skills. ”
“Their team has given us strong learning opportunities, and their developers are accommodating and collaborative.”

“We’re satisfied with the quality of work Computools deliver. They listen and try to understand our needs instead of finding new ways to charge us. We appreciate their transparent work structure. They kept us up-to-date regarding their progress throughout the entire development cycle. Knowing the system’s status throughout the coding process put my mind at ease.”
“They are very accommodating. They have very talented people. I’ve worked with hundreds of overseas developers and it’s not normal to have such excellent overseas developers. I don’t have to babysit Computools. They speak great English. They’ve also really helped with making suggestions on how to improve the product.
When we first launched our product at the beginning of the year, we were at 30,000 users a month and now we’re at 70,000. The bump in users is a result of the increased option rate and the new toys that Computoolls have built for me.”

“Computools developed software for our business to help automate our processes. Their team is very easy to speak to over Skype, where I can speak directly to a designated client manager, project manager, and the development team.”

“They were able to reduce the customer entry acquisition process from 2–3 weeks to 48 hours and have completely optimized all business processes. They’re a trustworthy company, full of integrity and great principles. They also communicate well in spite of the distance and resolve problems quickly.”

“They have a very positive attitude, which I enjoy a lot, and their technical skills are impressive. During this project, I got acquainted with their VP in charge of technical development, and he’s very impressive. Technologically, they are on the cutting edge of what they do. They use a lot of interesting technologies, which is good.”
Because decisions made in the barnyard now depend on data. With rising input costs, animal health risks, and growing traceability demands, software delivers the tools to manage livestock proactively, not reactively.
Yes. Smart software tracks health indicators, flags abnormal patterns, automates vaccination alerts, and centralizes treatment histories, turning routine data into an early warning system for herd health.
Yes. Computools enables seamless integration with RFID tags, GPS trackers, smart collars, feeding systems, and environmental sensors, offering complete visibility and automation across the farm.
Yes. By integrating with IoT sensors and farm machinery, Computools platforms track methane output, manure management, and grazing cycles, turning carbon footprints into measurable metrics that support certification and compliance.