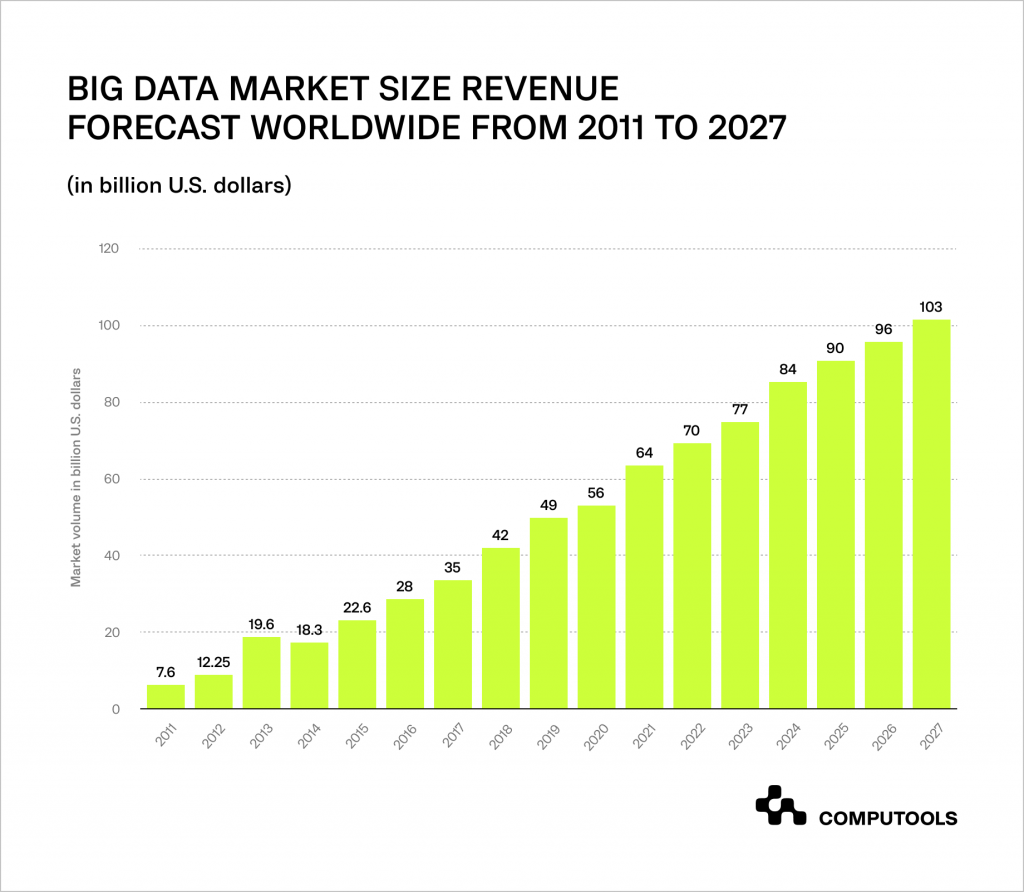
Statista predicts that the global Big Data market will grow to $103 billion by 2027, more than double its size in 2018. By then, the software will account for 45% of the total market.
Big Data is a term used to describe datasets that are too big or complicated to handle using conventional techniques.
The definition of these datasets comes from:
• High volume (lots of data),
• High velocity (fast-moving data),
• High variety (many types of data).
The growth of mobile data, cloud computing, and technologies like AI and IoT are making data bigger and more complex. This creates a demand for better tools to process it.
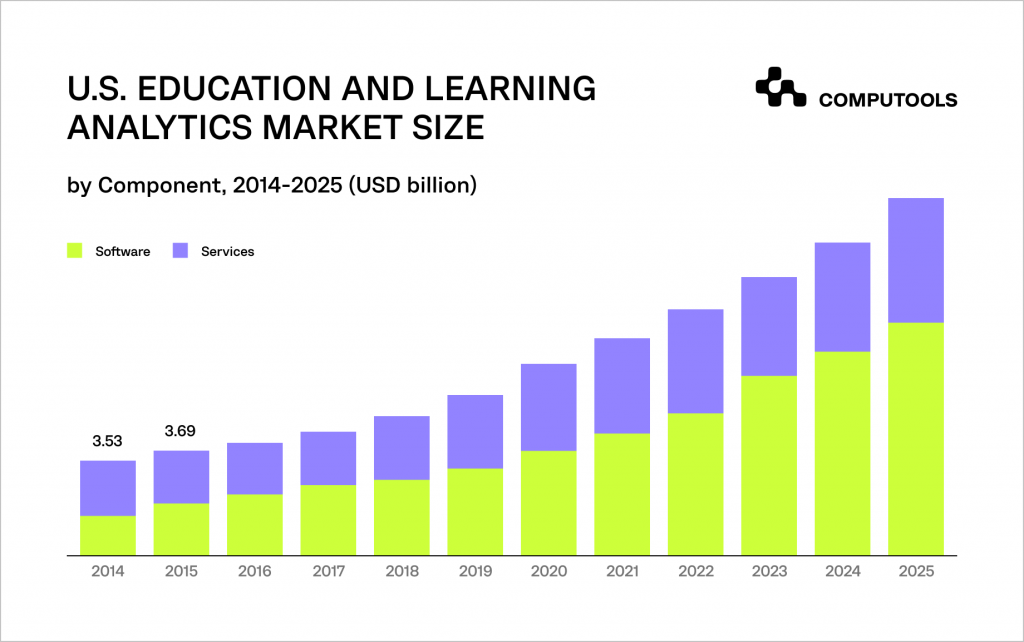
The market for education and learning analytics was estimated to be worth USD 17.01 billion in 2018, and between 2019 and 2025, it is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.4%.
The main factor driving the market for education and learning analytics is the growing awareness of the potential of learning analytics to change or improve a learning system in response to student performance or, in a corporate context, to improve the performance of educational institutions.
The Growing Use of Technology in Education and Business
Big Data in education is very important because it helps track how well students or employees in a company are learning and performing. The importance of data in education cannot be overstated, as it helps businesses assess how well their training programs are functioning and whether they are boosting employee productivity. It also helps businesses figure out which programs are successful and which ones are not helping.
3D animation enhances the clarity and visualization of information, further improving the effectiveness of learning analytics programs.
For instance, Alteryx introduced a feature that allows for visual representation of data through charts and graphs, helping data scientists analyze critical business information more quickly and efficiently. As demand for such interactive solutions continues to rise, the future of Big Data analytics services looks promising.
In education, various technologies such as mobile devices, student data management systems, lecture recording, and learning platforms are being used more frequently.
This helps gather a lot of data about the learning process. These technologies improve educational systems and student outcomes.
By customizing learning experiences to each student’s requirements, educators may maximize the effectiveness of their teaching strategies and material delivery using Big Data in education.
This shift from a generic curriculum to personalized learning strategies exemplifies the profound effect that data has on enhancing student engagement and achievement.
Real-Life Examples of Big Data in Education
Big Data analytics in education has significantly enhanced student outcomes across various educational institutions by personalizing learning experiences, improving resource allocation, and enabling timely interventions. A range of examples of predictive analytics in education illustrates the transformative power of data-driven strategies in real school settings.
Analytics plays a key role in personalized learning. For instance, a high school implemented Big Data and education technologies to track student performance trends through tests and assignments. By identifying struggling students early, educators provided targeted interventions that enhanced learning experiences and outcomes. Such strategies showcase how real-time data usage fosters a culture of academic support and improvement.
Integrating data analytics for schools helps in curriculum tailoring. One institution used data analytics to enhance course scheduling based on student preferences and enrollment trends. This initiative led to higher satisfaction levels among students and improved academic outcomes within various departments. By implementing timely interventions driven by detailed data analysis, institutions significantly reduced dropout rates and ensured academic success for every student. Early identification allows for a more adaptive educational approach that benefits individual learners.
Learning analytics in vocational education provides further evidence of the power of Big Data analytics in education. City & Guilds, operating across approximately 80 countries, utilizes xAPI-driven learning analytics to bridge skills gaps. The integration of multiple systems helps tutors predict areas of risk in learner progress, allowing for timely interventions. This application serves as a comprehensive model illustrating how Big Data and education intersect to guide skill development and recognition within vocational settings.
At Universitas Hindu Indonesia, researchers found a significant positive correlation between data-driven strategies and personalized learning experiences. Their study emphasized the role of Big Data analytics for education in offering individualized learning opportunities, further reinforcing data’s critical role in enhancing educational outcomes.
Moreover, Big Data and education are advancing teacher training initiatives. In China, a new AI model utilizing deep learning was developed to optimize training for early childhood education (ECE) teachers. Such innovative applications of data in teacher education can directly impact student outcomes in the classroom.
Finally, data-driven strategies also enhance operational improvements for better decision-making. Indiana University implemented a data management platform to enhance decision-making processes through improved data management and analysis models. This initiative exemplifies how data analytics for schools improves resource allocation and educational effectiveness, emphasizing the critical role of Big Data in the education industry.
Why Some EdTech Fails
1. Legal Challenges
Educational institutions are navigating complex data protection laws, such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (USA) and General Data Protection Regulation (EU).
Critical questions include: Which data can be used? Who owns and can access the data?
The combination of different datasets can make it difficult to ensure anonymity, raising concerns about whether privacy can truly be maintained in the age of big data.
2. Ethical and Social Challenges
Ethical concerns revolve around the data trails left by individuals and the potential future consequences of data use, such as profiling or stigmatization. For example, low grades from high school shouldn’t be used to affect future opportunities.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on data could alienate students if their digital identity replaces personal interactions. There’s also concern over increased inequality, as those with better access to technology (e.g., Wi-Fi) may benefit more from big data analytics than those without.
3. Technological Challenges
A major obstacle is the availability and quality of data. Educational institutions often collect large amounts of data without clear goals or questions, leading to data-driven rather than question-driven research.
Additionally, data integration issues arise due to the difficulty of connecting different datasets, ensuring data formats align, and preprocessing data. Data quality issues, such as bias, missing data, and errors, further complicate the use of big data.
4. Data Ownership and Accessibility
Ownership of data affects accessibility for research and decision-making. Often, stakeholders are hesitant to share data without strict conditions, such as ensuring anonymity and limited usage.
Moreover, General Data Protection Regulations restrict data usage to predefined goals, making it harder to adapt to new research needs.
5. The gap between business executives and educators
Teachers and business entrepreneurs think in distinct ways. To get their EdTech software development on the market, most founders put in a lot of effort. They aim to test their hypotheses as soon as possible, collect input, and adjust course as needed. They use sales goals and company growth as indicators of success.
Conversely, teachers like to proceed cautiously. They are concerned about how such a product would affect pupils and how much more work it will require to implement. Teachers talk about student achievement, whereas business executives talk about data. This discrepancy obscures legitimate business prospects and makes it difficult to market big data examples in real life.
Companies hurry to design products based on preconceptions rather than taking the time to learn the real requirements of instructors and students. These products frequently fall short because they demand more work or a behavioral shift from the teachers.
The greatest chance is to comprehend the shortcomings of the existing framework in order to create a solution that will naturally find its way into classrooms. Speaking with teachers, seeing them at work, and asking lots of questions are some of the greatest methods to find out about such restrictions.
Education professionals may be a valuable network to establish connections with. This will provide many opportunities for edtech to hear about their problems, share ideas with others, and receive insightful feedback.
6. Technological Availability
The second noteworthy difficulty is one that all educators, regardless of their field, are all too familiar with. It is the teacher’s responsibility to minimize the apparent gap between students’ financial situations and abilities. And when technology comes into play, the disparity widens even further.
This gap threatens the widening educational disparities in a society where EdTech is becoming the norm. It is common for students from underprivileged neighbourhoods to lack the dependable internet connections and gadgets needed for online education.
In reality, government involvement is necessary to promote social fairness because educational institutions cannot solve this problem on their own. However, there are a few actions one can do to optimize the educational platform to be more flexible until that bigger aim is accomplished.
One can modify an EdTech system to enable low-bandwidth situations, for instance. Making the UI sufficiently accessible to enable even pupils who aren’t frequent internet users to use it without any prior digital knowledge is another recommendation.
7. Integration and Training of Teachers
A significant obstacle in using Big Data in higher education in 2024 is guaranteeing that teaching staff has the requisite information and comprehension to optimise its utilisation.
Furthermore, they need to be so knowledgeable about the platform that they can instruct their pupils in its use as well.
Fortunately, many educators are willing to use new technology; more than 70% of them said they intended to use artificial intelligence (AI) in their classes next year.
However, there are several kinds of educators in schools, some of which favor conventional approaches. This is why it is essential to implement teacher training programs; not only will they increase their knowledge, but maybe also their optimism.
Doing this task is not at all simple. To make sure that the new procedures are being used effectively, a substantial amount of time and resources must be set aside. Otherwise, if teachers aren’t going to utilize all the features of EdTech tools, what purpose is it to invest in them?
Teachers will require continuous assistance to complete this next phase effectively. One strategy would be to collaborate with EdTech experts or IT departments that offer round-the-clock support and Big Data consulting in the integration procedure.
It will require time to become used to the innovations, so make sure you create targets that account for this in addition to allocating resources for training and appropriate support.
8. Insufficient Learning Opportunities
Giving students a customized learning experience might make all the difference in how well they recall the new information and how they see your school. Consequently, your dissatisfied students may cost you money if, for instance, you are a non-mandatory educational institution (online classes, university, or something similar).
Though it’s not always the case, educational technology has the potential to assist customize students’ learning paths. Sadly, a lot of the EdTech solutions that are now on the market are copycat versions of one another and are beginning to resemble old teaching techniques that have been updated for a computer screen.
You have to conquer this obstacle if you want to genuinely stand out in your field and be acknowledged as a leader. Creating and implementing specialized learning platforms is the answer. In this manner, you’re utilizing the potential to completely transform education by enabling customized learning experiences that are dynamically adjusted to meet the requirements of every individual student.
To overcome the limitations of generic EdTech solutions and truly stand out, it’s crucial to invest in platforms that deliver personalized learning experiences tailored to individual students. Without a customized approach, you risk losing students and falling behind competitors who are embracing this innovation.
The key to success lies in partnering with professionals who understand the nuances of education technology and can deliver solutions that genuinely enhance learning outcomes.
This is where Computools excels—offering expertise in developing innovative, secure, and flexible platforms that meet the evolving needs of the education sector.
Why Choose Computools for Your Education Software Engineering Needs?
At Computools, we’re thrilled about the progress we’ve made in the education sector through innovative EdTech software development for our clients. One of the case studies we’re particularly proud of is the Teacher’s Dashboard.
This platform makes it easy for teachers in Norway to share and improve educational content. With its simple design and fun features, the aim is to make learning engaging and accessible. Plus, it allows students to follow customized learning paths by using smart algorithms that adapt to each learner’s needs.
Another project is BeEducated, an online platform that offers a variety of learning services for students. We built the entire tech setup for this project, ensuring it’s robust and flexible to meet the changing demands of education.
Since we started in 2013, Computools has grown rapidly, working with clients around the globe. For several years, we’ve made it onto the Top Global Outsourcing 100 list by IAOP, and we’ve successfully completed over 350 projects in more than 20 countries. This shows our ability to handle a wide range of software development challenges.
When our partners choose Computools, they can trust that they have a reliable ally. We focus on delivering solid IT operations and data security, following international standards like ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 27001:2013. This commitment ensures that our clients’ data is protected and compliant.
Contact our team at info@computools.com.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”